Learning Visual Basic for Applications is such an
empowering activity for anyone looking to expand their productivity,
automate repetitive tasks, or develop custom solutions within
Microsoft Office applications. With this guide, you will master the process of learning VBA
in an easy, step-by-step manner, regardless of whether you are a beginner or already have some
programming experience.

1. What is VBA and Why Learn It?
VBA is the programming language in Microsoft
Office that forms integration with applications such as Excel,
Word, Access, and Outlook. It will further help develop macros and give solutions targeted at an issue. The following are some reasons why VBA would prove valuable:Automation:
Eliminate repetitious tasks, such as generating reports or
cleaning up data
- Customization:
Adapt software for unique purposes beyond the out-of-the-box
solutions handle.
- Versatility: Interact from one office application to another, such as transferring data from
Excel into Word.
- Career Booster: VBA skills are required in the industries of data
analytics, finance, and project management.
2. Setting Up Your Environment
To get started, you need to enable the tools and set up
the environment where you’ll write and test VBA code.
Enabling the Developer Tab
- Open
Excel (or another Office application).
- Navigate
to File > Options > Customize Ribbon.
- Check
the Developer box in the right-hand pane and click OK.
Opening the VBA Editor
- Press
Alt + F11 to launch the VBA Editor.
- Familiarize
yourself with its layout, including the Project Explorer, Properties
Window, and Code Window.
3. Learn the
Basics of VBA
Understanding
Key Concepts
- Object Model: Learn how VBA interacts with
Office applications through objects like Workbooks, Worksheets, and
Ranges.
- Properties and Methods: Objects have
properties (characteristics) and methods (actions). For example, Range("A1"). Value
= 10 sets the value of cell A1 to 10.
- Variables and Constants: Use variables to
store data and constants for fixed values. For example:
Working with
Macros
Macros are small
programs written in VBA to automate tasks. Start by recording a macro:
- Go to Developer > Record Macro.
- Perform a simple task, like formatting cells.
- Stop recording and examine the generated code in
the VBA Editor.
4. Structured
Learning: A Step-by-Step Approach
Step 1: Learn
Basic Syntax
Understand VBA's
syntax rules, including:
- Declaring variables (Dim x As Integer)
- Writing comments (' This is a comment)
- Using loops and conditionals:
Step 2:
Explore Loops and Conditions
Loops and
conditions are essential for handling repetitive tasks and making decisions.
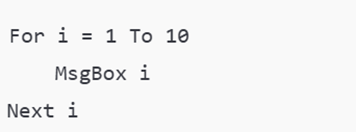
- For Loop:
- While Loop:
Step 3:
Understand Ranges and Worksheets
VBA is often
used to manipulate Excel worksheets. Learn to select ranges, add sheets, and
perform operations:
Step 4:
Master Procedures and Functions
Procedures are
blocks of code that perform tasks, while functions return values.
- Sub Procedure:
- Function:
5. Real-World
Applications
Automation of
Reports
- Generate monthly reports by fetching data, applying
formulas, and formatting automatically.
Data Cleaning
- Remove duplicates, standardize formats, and filter
data programmatically.
Custom
Dashboards
- Combine VBA with Excel’s visual tools to create
interactive dashboards.
Cross-Application
Integration
- Use VBA to transfer data from Excel to Word or send
automated emails via Outlook.
6. Advanced
Topics
Error
Handling
Handle runtime
errors gracefully using On
Error statements.
User Forms
Create custom
input forms for data collection and validation.
Database
Connectivity
Connect VBA to
external databases like SQL Server using ADO for advanced data manipulation.
7. Resources
for Learning
Books
- "Excel VBA Programming for Dummies"
by Michael Alexander.
- "Mastering VBA for Microsoft Office
365" by Richard Mansfield.
Online
Platforms
- Microsoft Learn: Comprehensive
documentation.
- YouTube Channels: Channels like ExcelIsFun
and Wise Owl Tutorials.
- Forums: Engage with communities like MrExcel or Stack Overflow.
Interactive
Learning
- Platforms like Udemy and Coursera offer guided
courses with projects.
8. Tips for
Success
Practice
Regularly
Apply your
knowledge to real-world scenarios. Automation tasks at work can be a great
practice field.
Build
Projects
Create projects
like invoice generators, data analysis tools, or report dashboards.
Collaborate
Join VBA
communities to learn from others' experiences and share your own.
Stay Updated
As Office
applications evolve, VBA also receives updates. Keep learning to stay ahead.
9. Common
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Debugging
Code
Use the VBA
Editor's debugging tools, such as breakpoints (F9) and the Immediate Window.
Understanding
Errors
- Syntax Errors: Ensure correct spelling and syntax.
- Runtime Errors: Handle these using error-handling
techniques.
Balancing
Complexity
Start simple.
Gradually tackle more complex tasks as your confidence grows.
10. Why VBA
Remains Relevant
Despite
competition from tools like Python and Power Query, VBA’s integration within
Office applications and its simplicity for non-developers make it an
indispensable skill.
By following
this guide and dedicating time to practice, you’ll gain proficiency in VBA and
unlock new levels of productivity. If you have specific questions or need
assistance with projects, feel free to ask!